Before Sara Josephine Baker took charge, a third of children died before their 5th birthdays.
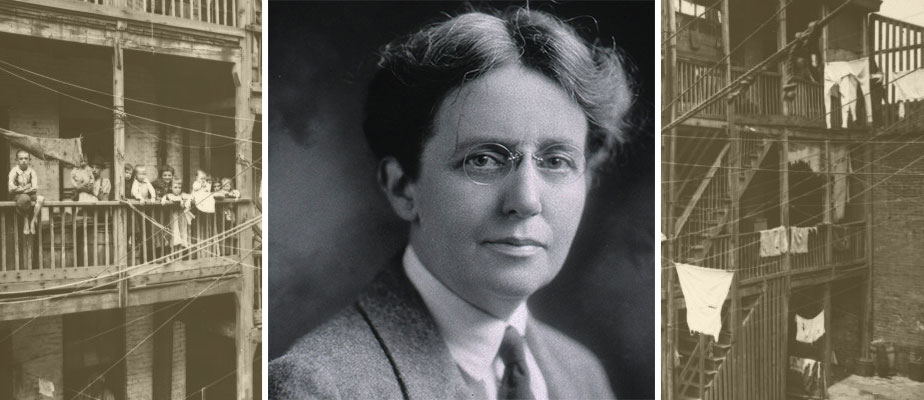 At the beginning of the 20th century, the pioneering physician Sara Josephine Baker revolutionized public health care for children in New York City. When Baker started her public health work, the impoverished slums of Hell's Kitchen on the city's West Side were among the most densely populated places on Earth, and epidemics killed an estimated 4,500 people each week in the overcrowded immigrant tenements, including 1,500 babies. With a third of children born there dying before their fifth birthday, Baker famously remarked that "It is six times safer to be a soldier in the trenches than a baby in the United States." Thanks to her initiatives, the death rate plummeted, and Baker became famous as doctor who had saved 90,000 children in New York City and countless others as her reforms were replicated across the United States and in other countries. Continue reading Continue reading
At the beginning of the 20th century, the pioneering physician Sara Josephine Baker revolutionized public health care for children in New York City. When Baker started her public health work, the impoverished slums of Hell's Kitchen on the city's West Side were among the most densely populated places on Earth, and epidemics killed an estimated 4,500 people each week in the overcrowded immigrant tenements, including 1,500 babies. With a third of children born there dying before their fifth birthday, Baker famously remarked that "It is six times safer to be a soldier in the trenches than a baby in the United States." Thanks to her initiatives, the death rate plummeted, and Baker became famous as doctor who had saved 90,000 children in New York City and countless others as her reforms were replicated across the United States and in other countries. Continue reading Continue reading